RESEARCH
E. COLI
Antimicrobial activity of Constructive Microbes against the bacterium Escherichia coli
Final conclusion
The Constructive Microbes display a strong bactericidal activity against Escherichia coli manifesting itself as a complete inactivation of 99.995 – 100% of the bacterial cells after a 24h treatment and 100% cells after a 48h treatment.
I. General information
The test was carried out in the period of 7.11 – 21.11. 2023, on the reference strain Escherichia coli ATCC25922 (fermenting the sugar lactose). For counting living cells of E. coli, a selective and differential medium (MacConkey agar) was used. The medium contains components inhibiting growth of Gram-positive bacteria (crystal violet, bile salts) and a differential component (lactose). Lactose-fermenting (lactose-positive) strains of E. coli after 24 h of incubation form red-to-pink colonies, 2-3 mm in diameter (fig. 1.).

Fig. 1. Growth of lactose-positive colonies of Escherichia coli on MacConkey agar. One tenth ml of the saline suspension of the strain tested was inoculated on the plate.
II. Inoculation of Constructive Microbes on MacConkey agar
Because Constructive Microbes constitute of a mixture of living cells of a number of bacterial species, in the first step of the experiment the liquid (diluted 1:10 and 1:100) was applied on MacConkey agar. The medium was incubated aerobically at 30°C for 48 hours. After 24 hours incubation, the growth of very numerous, small, lactose-negative colonies (less than 0.5 mm in diameter, fig. 2.), as well as of moderately numerous colonies of 1.5 - 2 mm in diameter (also lactose-negative) was found. There were no lactose-positive colonies detected on the medium. Thus, MacConkey agar could be used in the further steps of the experiment and any evidence of lactose-positive colonies would result exclusively from the presence of living cells of Escherichia coli added to the liquid.
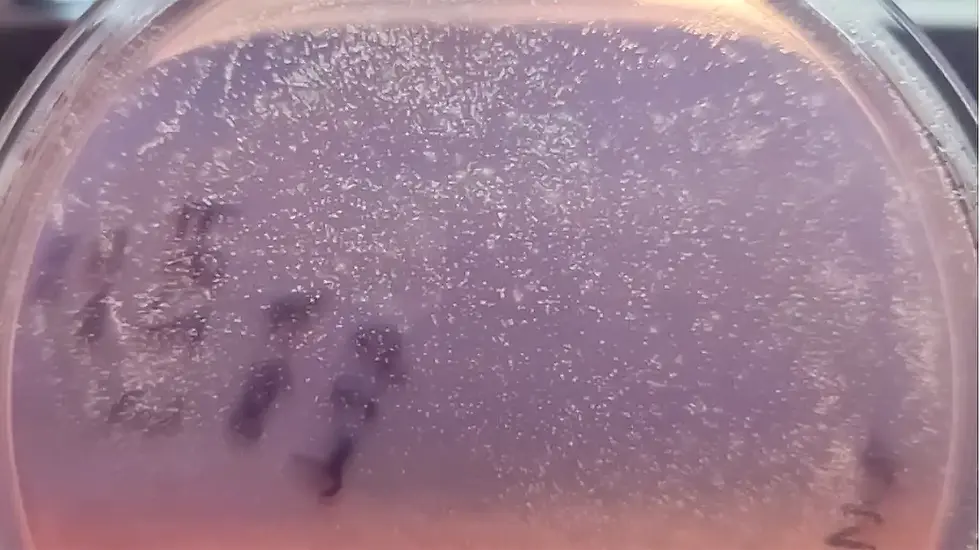

Fig. 2. Growth of bacteria from Constructive Microbes on MacConkey agar (dilution 1:100, incubation time: 24 h). Only small, lactose-negative (colourless) colonies can be seen.
III. Preparation of E. coli suspension
Culture of E. coli, grown on tryptic-soy agar, was mixed with saline to obtain a suspension corresponding to 0.5 of the McFarland turbidity standard. Next, in order to count the number of cells, this suspension was diluted 1:10,000 and 1:100,000 and 0.1 ml of each dilution was transferred onto a Petri dish with tryptic-soy agar. Based on numbers of colonies grown, the concentration of E. coli cells was calculated to be 5.4 x 107/ml.
IV. Assessment of the activity of Constructive Microbes against E. coli
The suspension of E. coli prepared as described previously (0.5 of the McFarland standard) was mixed with the undiluted Constructive Microbes liquid at the 1:1 ratio (2ml of E. coli suspension + 2ml of liquid) and allowed to interact at room temperature. After 24 and 48 hours, as well as 5 days of the test, 0.5 ml of the mixture were diluted 1:10, 1:100, and 1:10,000 with saline and 0.05 – 0.1 ml of each dilution were inoculated onto MacConkey agar. The plates were then incubated at 37°C for 24 hours. At each time assessed, the number of living cells of E. coli was calculated based on numbers of lactose-positive colonies grown on the medium. For a greater reliability of results, the procedure described in the points III and IV was carried out in duplicate.
In the first series of the experiment, already after 24 hours of incubation of E. coli suspension with 1:10. The growth has also not occurred after 48 hours and 5 days of incubation with . Thus, the liquid tested has inactivated 100% of E. coli cells as rapidly as within 24 hours.
In the repeat experiment, after 24 hours of incubation of E. coli suspension with Constructive Microbes, no growth of the bacterium was found at the dilution 1:10 but one lactose-positive colony was detected at 1:100 (fig. 3). This fact may have resulted from either an accidental transfer of one E. coli cell while making serial dilutions or contact inhibition of the microorganism by the more concentrated (i.e., 1:10) Constructive Microbes liquid directly on the medium surface.
Even if the presence of one E. coli colony at the 1:100 dilution is not an accident, the number of living cells of the microorganism after 24h treatment with Constructive Microbes would be 2 x 103 what is equivalent to a 99.995% reduction of the original number of cells.
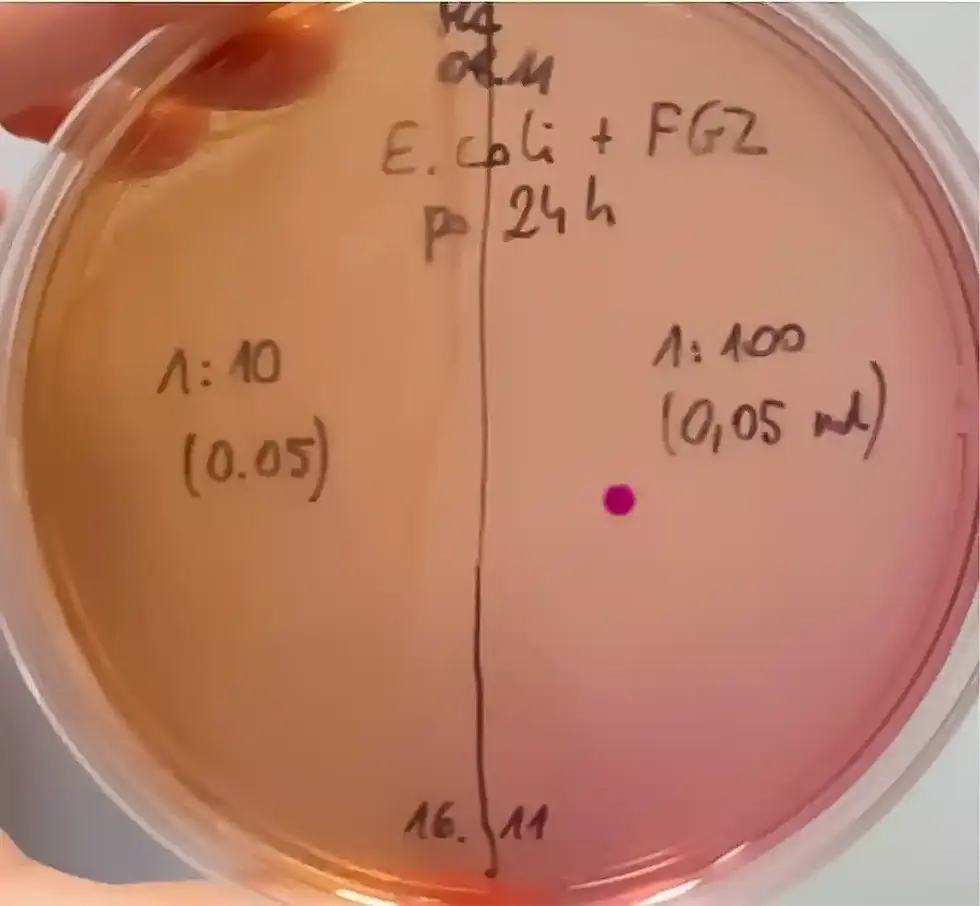
Abb. 3. MacConkey-Agar inokuliert mit E. coli-Suspensionlactose-negative Kolonien zu sehen, während in der Verdünnung 1:100 eine lactose-positive Kolonie (typisch für E. colinnung 1:10 sind zahlreiche kleine, lactose-negative Kolonien zu sehen, während in der Verdünnung 1:100 eine lactose-positive Kolonie (typisch für E. coli) nachgewiesen wurde.
